You are leaving this site!
By clicking YES, you will be directed to another website. Click NO to remain on this page. Do you wish to continue to another website?
This website sets cookies on your computer, to give you the best experience by personalizing your content and analyzing traffic. Without cookies, the site won’t function as expected. If you want to learn more, please read our Privacy Policy or Cookie Policy.
By closing this message, you consent to the use of cookies on this device.
Intended For US Audiences Only.

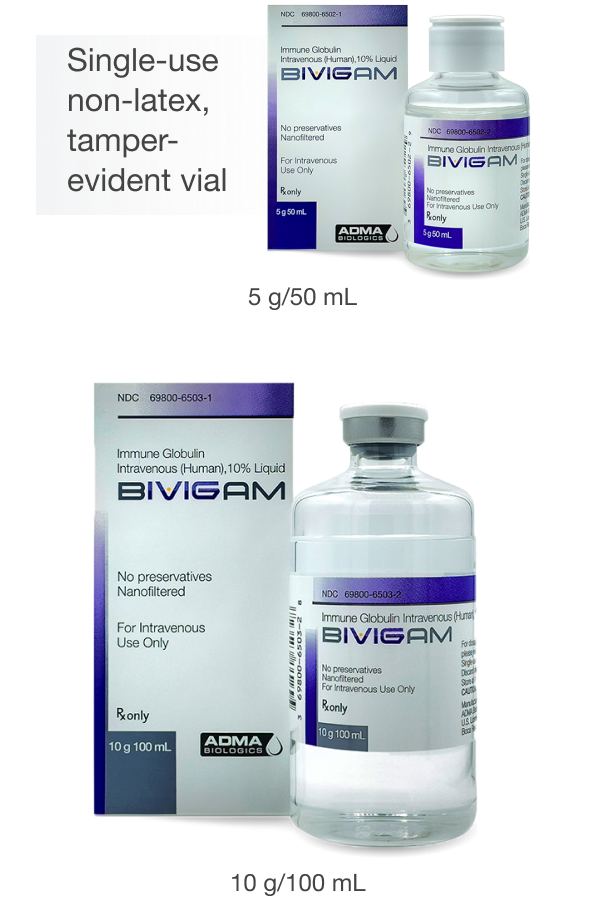
BIVIGAM is a purified, sterile, sugar-free, glycine-stabilized liquid solution containing 10% IgG (100 mg/mL) for intravenous infusion1
*Frequency/amount of IgG therapy may vary from patient to patient. The proper amount can be determined by monitoring clinical response.
0.5 mg/kg/min
(0.005 mL/kg/min)
Increase gradually
every 20 minutes (if tolerated)
by 0.8 mg/kg/min up to 6 mg/kg/min
BIVIGAM is an Immune Globulin Intravenous (Human), 10% Liquid, indicated for the treatment of adults and pediatric patients 2 years of age and older with primary humoral immunodeficiency (PI). This includes, but is not limited to, the humoral immune defect in common variable immunodeficiency (CVID), X-linked agammaglobulinemia, congenital agammaglobulinemia, Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, and severe combined immunodeficiencies (SCID).
Important Safety Information for BIVIGAM®
WARNING: THROMBOSIS, RENAL DYSFUNCTION, AND ACUTE RENAL FAILURE
Contraindications
BIVIGAM is contraindicated in:
Warnings and Precautions
Thrombosis may occur following treatment with immune globulin (IGIV) products, including BIVIGAM. Thrombosis may occur in the absence of known risk factors. Consider baseline assessment of blood viscosity in patients at risk for hyperviscosity and ensure adequate hydration before administration. For patients at risk of thrombosis, administer BIVIGAM at the minimum dose and infusion rate practicable. Monitor for signs and symptoms of thrombosis and assess blood viscosity in patients at risk for hyperviscosity.
Severe hypersensitivity reactions may occur with IGIV products, including BIVIGAM. In case of hypersensitivity, discontinue BIVIGAM infusion immediately and institute appropriate treatment. Medications such as epinephrine should be available for treatment of acute hypersensitivity reactions. Patients with known antibodies to IgA may have a greater risk of developing potentially severe hypersensitivity and anaphylactic reactions.
Acute renal dysfunction/failure, osmotic nephrosis, and death may occur upon use of human IGIV products. Ensure that patients are not volume depleted before administering BIVIGAM. Periodic monitoring of renal function and urine output is particularly important in patients judged to be at increased risk of developing acute renal failure. Assess renal function, including measurement of blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and serum creatinine, before the initial infusion of BIVIGAM and at appropriate intervals thereafter. If renal function deteriorates, consider discontinuing BIVIGAM. In at-risk patients, administer BIVIGAM at the minimum infusion rate practicable.
Hyperproteinemia, increased serum viscosity, and hyponatremia may occur in patients receiving IGIV treatment, including BIVIGAM. It is critical to clinically distinguish true hyponatremia from a pseudohyponatremia that is associated with or causally related to hyperproteinemia. Treatment aimed at decreasing serum free water in patients with pseudohyponatremia may lead to volume depletion, a further increase in serum viscosity, and a possible predisposition to thrombotic events.
Aseptic meningitis syndrome (AMS) may occur with IGIV treatments, including BIVIGAM. AMS usually begins within several hours to 2 days following IGIV treatment. AMS may occur more frequently in association with high doses (2 g/kg) and/or rapid infusion of IGIV. Conduct a thorough neurological examination on patients exhibiting signs and symptoms of AMS, including cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) studies, to rule out other causes of meningitis.
IGIV products, including BIVIGAM, may contain blood group antibodies that can act as hemolysins and induce in vivo coating of red blood cells (RBCs) with immunoglobulin, causing a positive direct antiglobulin reaction and, rarely, hemolysis. Monitor patients for clinical signs and symptoms of hemolysis, including appropriate confirmatory laboratory testing.
Noncardiogenic pulmonary edema may occur in patients following IGIV treatment, including BIVIGAM. Transfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury (TRALI) is characterized by severe respiratory distress, pulmonary edema, hypoxemia, normal left ventricular function, and fever. Symptoms typically appear within 1 to 6 hours following treatment. Monitor patients for pulmonary adverse reactions. If TRALI is suspected, perform appropriate tests for the presence of anti-neutrophil antibodies in both the product and the patient’s serum. TRALI may be managed using oxygen therapy with adequate ventilatory support.
Because BIVIGAM is made from human blood, it may carry a risk of transmitting infectious agents, e.g., viruses, and theoretically, the Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) agent. All infections suspected by a physician to possibly have been transmitted by this product should be reported to ADMA Biologics at 1-800-458-4244.
After infusion of immunoglobulin, the transitory rise of the various passively transferred antibodies in the patient’s blood may yield positive serological testing results, with the potential for misleading interpretation. Passive transmission of antibodies to erythrocyte antigens (e.g., A, B, and D) may cause a positive direct or indirect antiglobulin (Coombs’) test.
Pediatric Use
BIVIGAM was evaluated in 25 pediatric patients (3 children ages 2 to <6, 9 children ages 6 to <12, and 13 adolescents ages 12 to 16 years) with PI. The safety and effectiveness of BIVIGAM for the treatment of PI has been established in pediatric patients 2 years of age and older, based on data from 2 prospective, open-label, single-arm, multi-center studies, supported by evidence from a population PK analysis of adult and pediatric PK data.
Adverse Reactions
Serious adverse reactions observed in clinical trial subjects receiving BIVIGAM were vomiting and dehydration in one subject.
The most common adverse reactions to BIVIGAM (≥5% of clinical study subjects) were headache, fatigue, infusion site reaction, nausea, sinusitis, increased blood pressure, diarrhea, dizziness, and lethargy.
You are encouraged to report side effects of prescription drugs to ADMA Biologics at 1-800-458-4244 or the FDA. Visit www.fda.gov/MedWatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
For more information about BIVIGAM, please see full Prescribing Information.
References: 1. BIVIGAM Prescribing Information. Boca Raton, FL: ADMA Biologics; 2022. 2. Wasserman RL. A new intravenous immunoglobulin (BIVIGAM®) for primary humoral immunodeficiency. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2014;10(3):325-337. 3. Wasserman RL, Church JA, Stein M, et al. Safety, efficacy and pharmacokinetics of a new 10% liquid intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) in patients with primary immunodeficiency. J Clin Immunol. 2012;32(4):663-669.